Contents
What is Risk Management?
Risk management is a process applied in organizations to identify potential events. These occurrences are linked to situations that may affect the company, generating uncertainties that lead to problems or opportunities.
Its purpose is to help the company achieve its objectives, serving as an essential tool for the proper progress of strategic planning. Beyond identification, risk management also evaluates, classifies, and mitigates all potentially harmful issues.
In the context of maintenance, every company must perform risk management, regardless of its field or size. The approaches may vary depending on the sector, but the main objective remains the same: preventing accidents.
Steps to implement Risk Management
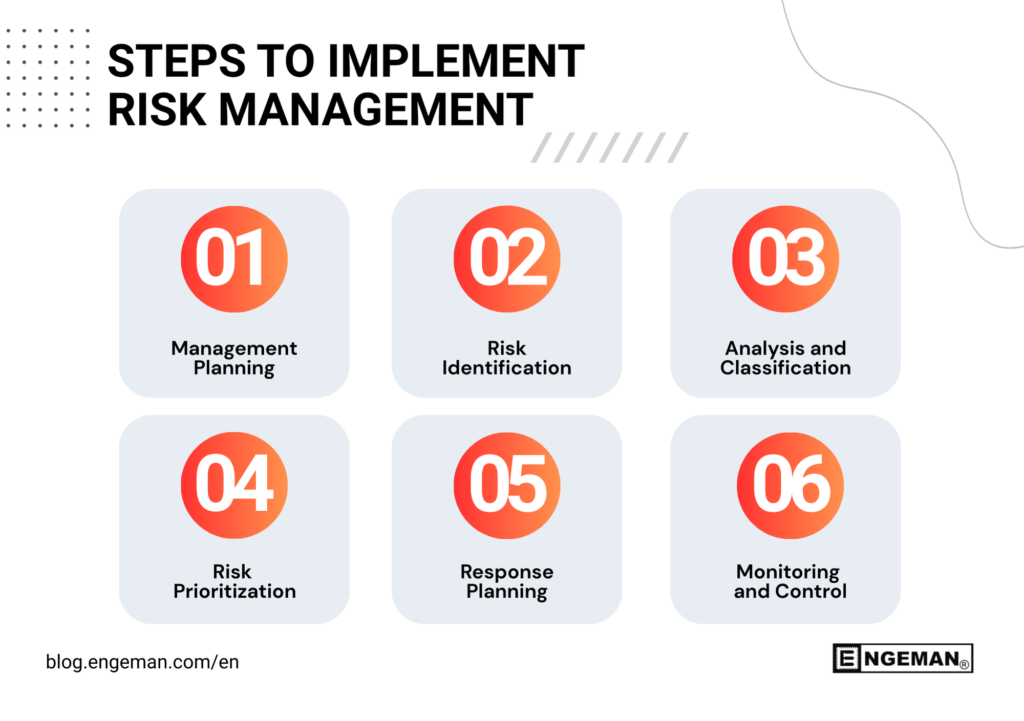
Below, follow in detail each step of implementing risk management in an organization:
1. Management Planning
The first step consists of planning the performance of risk management, monitoring, and control processes. This includes defining a specific methodology, delegating responsibilities and functions to the teams involved, and gathering budgeting and cost predictability information.
2. Risk Identification
This step involves creating a list of all uncertainties that could impact the performance of an activity or the success of a project. It identifies possible sources of risk for later resolution.
This mapping is fundamental for risk analysis and management, and all critical actions must be structured in detail. Generally, this list includes:
- supply chain;
- financial department;
- human resources;
- industrial facilities;
- marketing and sales processes;
- provision of direct services.
3. Analysis and Classification
At this stage, risks are analyzed and classified by evaluating their likelihood of occurrence and their impact on the production process. This information helps create parameters to categorize problems and define actions.
4. Risk Prioritization
Next, the risks are ranked based on the previous analysis. Risks with higher probabilities of occurrence and greater impacts should be prioritized for preventive action.
A probability-and-impact matrix can be used to classify risks and outline strategies as follows:
- Trivial risks: rare probability and insignificant consequences; action is only needed if they occur.
- Moderate risks: mitigation actions are required to reduce probability and impacts.
- Intolerable risks: require immediate actions to reduce or eliminate the likelihood of occurrence and related impacts.
5. Response Planning
At this stage, effective actions are defined to reduce or eliminate the probability of risks occurring. This includes mitigation strategies, corrective measures, and specific procedures for each case.
Investments should be directed toward eliminating root causes, fixing failures, and preparing structured plans to handle problems if they arise. It is also essential to designate those responsible for managing risks and containing potential losses.
6. Monitoring and Control
Finally, companies must monitor their activities and project progress to ensure that preventive measures are effectively applied. This continuous process also helps identify new threats and implement corrective actions when necessary.
How Engeman® can help with risk management
After implementing a risk management plan, it is essential to continuously monitor the strategy. If procedures deliver good results, only occasional adjustments may be required.
To ensure efficiency, it is essential to rely on a dedicated system, avoiding parallel controls. In the same way, teams must be trained to use the resources provided by such systems.
Engeman® implantation supports maintenance planning and approval flows. Documented procedures reduce improvisation, minimize deviations, and drastically cut down on incidents.
With Engeman®, organizations can reduce costs and optimize processes by analyzing machinery availability, production expenses, quality of activities, and operational safety.
Among the main benefits of adopting specialized maintenance software like Engeman®, the following stand out:
- efficient use of resources;
- planned maintenance;
- information sharing between production sectors;
- emergency maintenance plans;
- reminders for periodic equipment inspections;
- spare parts inventory control;
- maintenance history of equipment occurrences;
- quick access to information through graphs, reports, and performance indicators.
Conclusion
Risk management is a systematic process of strategic planning within organizations. Its goal is to identify, analyze, and respond to uncertainties, minimizing or eliminating negative impacts on the business.
To ensure efficient risk management, it is crucial to adopt effective control measures that optimize resources and improve responsiveness. Continuous monitoring is the only way to maximize results and enhance sector performance.
Engeman® is a software solution focused on maintenance planning and approval flows. It reduces improvisation, deviations, and accidents while maintaining a full history of equipment and procedures. This contributes directly to safer, more efficient operations and supports business growth.
Want to explore all the features of Engeman® in practice? Request a demo and learn more!




